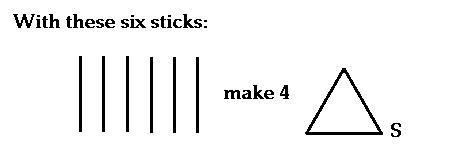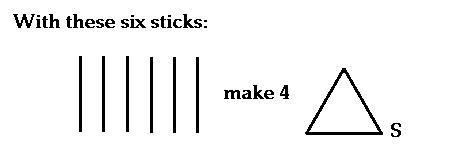THINKING
Updated:
2013-12-02
Test Items are in bold or bold
I. REPRESENTATION
- Representation
- Domain
- Context, i.e., "oh and two"
- Content
- features of the representation, i.e., categories--eye
color vs. gender
- Code
- relationship of representation to world, i.e., reading
and writing, languages, slang
- Medium
- required, but can change without destroying
representation (film vs. videotape)
- Dynamics
- changes over time, i.e., pawnbroker symbol, slang,
Baptist fish
II. PROBLEM SOLVING
- Definition
- "gap that separates the present state and the goal state"
(Hayes, 1978)
- I need to get to Little Rock.
- I'm in Magnolia = present state
- I need to be in Little Rock = goal state
- Understanding the Problem
- Understanding the problem
- Context
- Why the need to go to Little Rock?
- Emergency?
- Routine?
- Entertainment
- Shopping
- Operators (rules, moves, legality, reality)
- Well defined vs. Fuzzy
- Chess and other games
- Real world rules
- Walking?
- Driving
- Flying?
- Teleporting?
- Goal State
- Games
- Part of game
- Chess = capturing King
- Football = scoring most points
- Golf = taking least strokes
- Real world
- Location in Little Rock
- School
- Work
- Life
- Solving the problem
- Problem Space
- Path from initial state to goal state
- Number of paths
- Types of Solutions
- Algorithms
- Guarantee a solution
- How many desks in Peace Hall?
- How many desks at SAU?
- How many desks in Arkansas?
- How many desks in the World?
- All of the above problems solved by same
algorithm: count them
- Some algorithms do not work in real time
- Heuristics
- Do not guarantee a solution (hunches, guesses, or
experential attempts)
- Traveling Salesman Problem
- Subgoaling
- Divide problem into smaller parts
- get vehicle
- fill with fuel
- establish route
- drive to Prescott
- drive to second Rest Stop
- drive to Little Rock
- Means-Ends Analysis
- Reduce the distance between initial and goal
states
- Working Backwards
- Start at goal and work back to initial state
- Need to be in Little Rock by 5:00
p.m.
- It takes 2.5 hours to drive
- I need to get gas first (add 30
minutes)
- I need to take kids to school (add 30
minutes)
- Leave by 1:30 p.m.
- Analogies
- Similar problems may help solve current
problem
- I have never driven to Little Rock, but I
have driven to Dallas.
Much will be the same,
but some things (direction, roads) will
be
different.
- Restructuring
- Gestalt idea
- Mental Set
- How are these numbers arranged?
- 8, 5, 4, 9, 1, 7, 6, 3, 2, 0
- Solve the following problem:
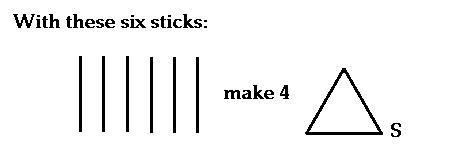
- Solution?
- Functional Fixedness
- Scheerer (1963) conducted an experiment where
he
manipulated the salience of a piece of string.
The more
salient it was, the more likely students
were to solve
the problem.
- Nearly all students knew they needed string
to
solve the problem. The solution was to tie
the
two sticks together to make them effectively
longer. Picture
- Insight
- Learning characterized by sudden realization
about
solution
- Incubation
- Delaying the problem solving process
- Works by:
- loss of detail and subsequent focusing on
important details
- better integration of recent and
pre-existing
memories
- weakening of mental sets
- relaxation
- take a day to plan trip to Little
Rock
- Creativity
- Divergent Thinking
- Finding many uses for object
- low frequency answers judged as
creative
- Convergent Thinking
- Linking several weakly associated elements into
one
correct concept (similar to crossword puzzle
thinking)
- Artistic and Scientific
- Christidou, Dimopoulos, and Kouladis (2004)
reported
that science was reported as a construct
that "...involves
inspiration, originality,
imagination and creativity, as
well as, skillful or
even artistic handlings;" (p. 352)
- Artistic creativity is difficult to study
- Investment Theory (Sternberg and Lubart)
- Buy low, sell high approach to ideas
- creativity is taking undervalued idea and
promoting
it, then "selling" it to a
now-understanding world
- think of Xerox, first invented in 1938
and not
made into a commercial product until
1959
III. REASONING
- Inductive Reasoning
- Coming to a conclusion from a series of observations
- Will the Sun rise tomorrow? Can you prove that?
- Confirmation Bias occurs when people attempt to verify
their beliefs instead of trying to falsify them
- Learning from experience, but in a very selective
fashion
- Deductive Reasoning
- Drawing conclusions from premises:
- All men are mortal. Aristotle is a man. Therefore,
Aristotle is mortal.
- Conditional Reasoning uses if...then statements
- Scientific Reasoning
- Scientists and Wason Selection task:
- Physicists (21-25% correct), Biologists (8-13% correct),
Psychologists (13-17% correct)
- Gambler's Fallacy: T T T T T T T T T ? (independent tosses)
- Disconfirmation may be better strategy in science
too
IV. DECISION MAKING
- Rationality
- Identify all reasonable alternatives
- Choices are transitive
- Maxixe utility
- Utility = is related to value, but modified by
psychological variables
- Consider relevant information
- Estimating Likelihoods of Occurrence
- Objective and Subjective Probabilities
- Objective are like dice and cards
- Subjective may not always be equal to objective (and
lower, usually)
- hot hand in basketball is subjectively higher than
real probability
- Heuristics (Kahneman & Tversky)
- Availability
- basing judgment of the frequency of events on the
ease
by which then can be brought to mind. For example:
doctors and nurses, police officers, shark attacks
- Illusory correlation: people overestimate the
likelihood
of simultaneous events
- Representativeness
- basing judgment of likelihood on the degree to which
the particular instance resembles a general class.
For
example: librarian, college professor, painter,
minister
- Anchoring-Adjustment
- The "anchor" is like a first impression. Later, the
anchor
is adjusted up or down as necessary. However,
anchor
often exerts undue influence
- Hindsight
- After the fact, people overestimate the
predictability of
an event. For example: the 9/11
attacks
- Critiques
- Heuristics are descriptive and atheoretical
approach
- Heuristics tend to be task specific
- Public Policy Decision Making: psychologists often inform
policymakers
- Cost/Benefit Analysis
- 100% safety is impossibility
- Known vs. statistical lives?
- Terrorism: How do you balance actual lives lost
vs.
potential lives lost?
- Economic vs. Non-economic costs?
- Facts vs. Values
- Policymakers are the ones who make ultimate
decisions
- Scientists make scientific recommendations to
policymakers
- accuracy vs. criterion measures
- Foreign Policy
- Groupthink
- Groupthink occurs when a cohesive in-group makes
decisions without considering other, suitable actions.
Janis (1972) cited the following conditions as
conducive
to groupthink:
- an isolated, powerful, decision making
group
- lack of impartial leadership
- high levels of stress on the group.
- Bay of Pigs
- Fix groupthink by
- encouraging criticism
- being impartial
- look outside itself for answers
- break up into smaller sub-groups,
each meeting
separately to consider other alternative
solutions.
- Economic Decision Making
- Economic theory (Bentham, 1789)
- Utility theory and Subjective Utility theory
- People make decisions strictly by economic
factors
- Homo economicus
- Bounded Rationality (Herbert Simon, Nobel Prize in
Economics, 1978)
- Prospect Theory (Daniel Kahneman, Nobel Prize in
Economics, 2002)
- "Satisficing" or responding to constraints
like: time, money, and resources
- Risk aversion: when dealing when gains, people
are risk averse
- Risk seeking: when dealing with losses, people
are risk seekers
- Cost traps: people who spend money already,
tend to keep spending even
when they should not
V. EXPERTISE
- Experts
- General characteristics of experts
- Unusually perceptive
- Discriminate between diagnostic and non-diagnostic
information
- Arrange information well
- Self-confident
- Creative
- Expertise
- Experts know 50,000 things
- experts can quickly recognize around 50,000
situations
- chess players
- medical diagnosticians
- In fields where knowledge exceeds 50,000 situations one
of two things happen:
- specialization
- Darwin was a naturalist, meaning he studied
nature,
today nature is too large to study as a field
thus
specializations: zoology, botany, microbiology,
entomology, etc.
- handbooks
- In fields like architecture and law, experts must
learn
how to look information up. Thus, architects and
lawyers
learn where to find the information they
need.
- Specific Expertise
- Chess
- Chase & Simon (1973)
- Master chess players only remembered board positions
better
than novices or class A players only when board
positions
were from master's chess games
- Master chess player's memory for random board
position
was no better than novices or class A players
(all had poor memory)
- shows chunking
- Physics
- Novices solved problems by working backward
- Experts solved problems by working forward
- Medical Diagnosis
- Obtaining information
- Generating hypotheses
- Interpreting data
- Evaluating hypotheses
- Both experts and novices use steps above, but experts
have more
complete database
- Expert Systems
- AI computer systems that make decisions
- Consists of:
- Inference engine: ability to use "if--then"
rules
- Specialized database
- Not as good as highest level human experts
- Better than average human experts
Back to Learning